Connecting multiple studio monitors to an audio interface can elevate your sound experience. It allows for better audio mixing and monitoring.
Many audio enthusiasts and professionals seek to enhance their sound setup. Adding multiple studio monitors is a great way to achieve that. This setup provides a more immersive audio environment, which is essential for accurate sound production. Whether you are a music producer, sound engineer, or just an avid listener, understanding this process is crucial.
By connecting multiple studio monitors, you can enjoy clearer, more detailed sound. It makes a significant difference in your audio projects. In this blog, we will explore the steps to seamlessly connect multiple studio monitors to your audio interface. Let’s dive into the world of enhanced audio setup.
Credit: www.abbeyroad.com
Choosing The Right Audio Interface
Connecting multiple studio monitors to an audio interface can feel daunting. The right audio interface is crucial for seamless integration and great sound quality. This guide will help you pick the best option for your setup.
Types Of Audio Interfaces
Audio interfaces come in various types, each serving different needs. USB interfaces are common and easy to use. They connect to most computers without issues. FireWire interfaces offer faster data transfer but need special ports. Thunderbolt interfaces provide high speed and low latency. They are ideal for complex setups. Some interfaces use PCIe cards, which fit inside your computer. These are great for professional studios.
Key Features To Consider
Several features matter when choosing an audio interface. First, consider the number of inputs and outputs. More inputs and outputs offer greater flexibility. Check the quality of the preamps. High-quality preamps improve sound clarity. Look for low latency performance. Low latency ensures real-time audio processing. Compatibility with your computer’s operating system is also important. Make sure the interface supports your preferred software. Portability might be a factor if you travel often. Smaller interfaces are easier to carry.
Understanding Studio Monitor Connections
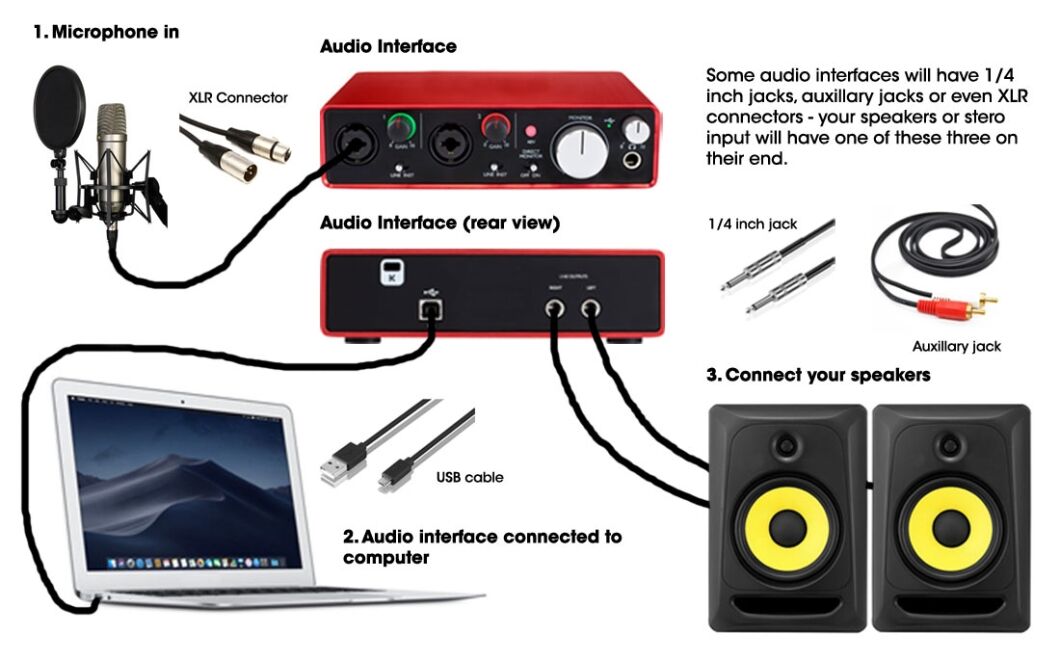
Understanding how to connect studio monitors to your audio interface is crucial for a seamless audio experience. This guide will walk you through the essentials of studio monitor connections, including the difference between balanced and unbalanced connections, and the common connector types you might encounter.
Balanced Vs Unbalanced Connections
Knowing the difference between balanced and unbalanced connections is important. Balanced connections use three wires: positive, negative, and ground. This setup helps to reduce noise and interference, making it ideal for professional audio environments.
Unbalanced connections, on the other hand, use just two wires: signal and ground. They are more susceptible to noise, especially over long distances. For short cable runs, unbalanced connections can still work well but are generally less reliable than balanced connections.
Common Connector Types
There are several types of connectors you might come across. The most common ones include:
- XLR: Often used for balanced connections. They are robust and secure.
- TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve): Also used for balanced connections. Similar in appearance to a standard headphone jack.
- RCA: Typically used for unbalanced connections. Common in consumer audio equipment.
- TS (Tip-Sleeve): Used for unbalanced connections. They look like a standard guitar cable.
Here is a quick comparison of these connectors:
| Connector Type | Balanced/Unbalanced | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| XLR | Balanced | Microphones, Professional Audio |
| TRS | Balanced | Headphones, Audio Interfaces |
| RCA | Unbalanced | Consumer Audio, Home Stereos |
| TS | Unbalanced | Instruments, Short Cable Runs |
Understanding these connections and their uses will help you set up your studio monitors effectively. Choose the right cables and connectors to ensure the best audio quality in your studio.
Setting Up Your Audio Interface
Connecting multiple studio monitors to your audio interface can seem tricky. But with the right setup, it becomes straightforward. This section will guide you through the process of setting up your audio interface. We’ll cover installing necessary drivers and configuring audio settings. Let’s get started.
Installing Necessary Drivers
Your audio interface needs drivers to work with your computer. These drivers help the interface communicate with your system. First, visit the manufacturer’s website. Look for the drivers section. Download the latest drivers for your model. Follow the installation instructions. This usually involves running an installer and restarting your computer.
Some interfaces come with a driver CD. You can use this, but downloading the latest version is better. The newer version may have important updates. Make sure your interface is connected to your computer during installation. This ensures the driver recognizes the hardware.
Configuring Audio Settings
After installing the drivers, configure your audio settings. Open your computer’s sound settings. Select your audio interface as the default playback device. This directs all sound output through the interface.
Next, open your digital audio workstation (DAW). Go to the audio settings or preferences. Choose your audio interface as the input and output device. This allows your DAW to send and receive audio through the interface.
Check the sample rate and buffer size. These settings affect audio quality and latency. A common sample rate is 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz. A lower buffer size reduces latency but uses more CPU power. Find a balance that works for your system.
Now, your audio interface is ready to use. You can connect your studio monitors and start creating. Enjoy the improved sound quality and control.
Connecting Studio Monitors
Connecting studio monitors to your audio interface is key for great sound. Proper connection ensures clear audio and accurate mixing. There are different ways to connect studio monitors. Below, we explore two common methods.
Using Xlr Cables
XLR cables are popular for connecting studio monitors. They provide balanced connections, reducing noise. XLR cables have three pins: positive, negative, and ground.
To connect using XLR cables:
- Identify the XLR output on your audio interface.
- Plug one end of the XLR cable into this output.
- Connect the other end to your studio monitor’s XLR input.
Repeat these steps for each monitor. Make sure connections are secure. This prevents signal loss and noise interference.
Using Trs Cables
TRS cables are another good option. TRS stands for Tip, Ring, Sleeve. They also provide balanced connections, reducing noise.
To connect using TRS cables:
- Locate the TRS output on your audio interface.
- Plug one end of the TRS cable into this output.
- Insert the other end into your studio monitor’s TRS input.
Repeat these steps for each monitor. Ensure the cables are plugged in firmly.
Here is a comparison table for XLR and TRS cables:
| Feature | XLR Cables | TRS Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Balanced | Balanced |
| Noise Reduction | High | High |
| Number of Pins | 3 | 3 |
| Common Use | Professional Studios | Professional and Home Studios |
Both XLR and TRS cables offer reliable connections. Choose based on your setup and preferences.
Configuring Monitor Placement
Setting up your studio monitors correctly is crucial for achieving great sound. Proper placement ensures you hear accurate audio. It helps with better mixing and mastering. In this section, we’ll discuss how to place your monitors for the best results.
Optimal Positioning
To start, position your monitors at ear level. This ensures you get a clear sound image. Use stands or shelves if needed. The tweeters should be at the same height as your ears.
Next, create an equilateral triangle between your monitors and your listening position. Each side of the triangle should be the same length. This setup helps in achieving a balanced stereo image. If your monitors are too far apart, you may lose the center image.
Here is a simple table to understand the placement better:
| Monitor Placement | Distance |
|---|---|
| Between Monitors | 3 to 5 feet |
| From Listening Position | 3 to 5 feet |
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Many people place their monitors too close to the walls. This can cause bass build-up. Keep at least 6 inches of space behind the monitors. This will help in reducing unwanted reflections.
Another common mistake is not angling the monitors correctly. Angle them towards your listening position. This ensures the sound is directed to your ears. Use the equilateral triangle setup as a guide.
- Do not place monitors on the same surface as your desk. This can cause vibrations and muddle the sound.
- Use monitor isolation pads to reduce vibrations. This helps in achieving clearer sound.
By paying attention to these details, you can improve your studio’s sound quality. Proper monitor placement is the first step towards better audio mixing.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Balancing Audio Levels
Balancing audio levels is essential when connecting multiple studio monitors to an audio interface. It ensures consistent sound quality and prevents distortion. Proper balance helps in creating an accurate mix. Below, we discuss two key methods for balancing audio levels effectively.
Adjusting Volume Control
Start by setting each monitor’s volume control to a similar level. This creates a baseline for balance. Use the interface’s output volume knobs to fine-tune each monitor. Listen carefully to ensure all monitors produce the same loudness. Adjust as needed to achieve uniform sound.
Using Audio Meters
Audio meters help in visually gauging sound levels. Most audio interfaces come with built-in meters. These meters show the output levels of each channel. Use them to match the levels of your monitors. Keep the levels within the green zone to avoid clipping. Consistent meter levels indicate balanced audio output.
Testing Your Setup
Once you have connected your studio monitors to your audio interface, it is crucial to test your setup. This step ensures everything works as intended and helps you spot any issues early. Let’s dive into the key aspects of testing your setup.
Playing Test Tracks
Start by playing some test tracks. Choose tracks you are familiar with. This helps you notice any discrepancies in sound quality.
- Play a track with a wide range of frequencies.
- Listen for clarity and balance.
- Ensure both monitors produce sound.
If you notice any issues, take note. It will help in the next steps.
Identifying And Fixing Issues
Once you have noted any problems, it’s time to identify and fix issues. Below is a simple table to help you troubleshoot common problems:
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| One monitor is silent | Loose cable connection | Check and secure all cables |
| Sound is distorted | Audio interface settings | Adjust levels on the interface |
| Uneven sound | Improper monitor placement | Reposition the monitors |
Follow these steps to resolve issues quickly. If problems persist, refer to your monitor and interface manuals for further guidance.
Credit: homedjstudio.com
Advanced Tips For Better Sound Quality
Connecting multiple studio monitors to your audio interface can enhance your mixing experience. But achieving better sound quality requires more than just plugging in the cables. Here are some advanced tips to help you get the best sound quality from your studio monitors.
Using Acoustic Treatment
Acoustic treatment helps control sound reflections in your studio. It minimizes unwanted echoes and improves sound clarity. You can use foam panels on walls, bass traps in corners, and diffusers on the ceiling. Place the foam panels where sound reflections are most likely to occur. Bass traps help reduce low-frequency build-up. Diffusers scatter sound waves, making the room sound more natural. These simple steps can greatly improve your listening environment.
Utilizing Software Plugins
Software plugins can enhance the sound quality from your studio monitors. Room correction plugins adjust the output to compensate for room acoustics. EQ plugins allow you to fine-tune frequencies to match your personal preference. Reverb plugins can add depth and space to your mixes. Using these plugins helps you achieve a balanced and professional sound. Always test and adjust plugins to suit your studio’s unique acoustics.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Connect Multiple Studio Monitors?
To connect multiple studio monitors, use an audio interface with enough outputs. Connect each monitor to an output using balanced cables.
Do I Need A Specific Audio Interface?
Yes, you need an audio interface with multiple outputs. Ensure it supports balanced connections for better sound quality.
Can I Use Unbalanced Cables?
Using unbalanced cables is not recommended. They are more prone to noise and interference. Always use balanced cables for better audio fidelity.
What Are Balanced Cables?
Balanced cables have three conductors: positive, negative, and ground. They help reduce noise and maintain signal integrity over long distances.
Conclusion
Connecting multiple studio monitors to an audio interface doesn’t have to be hard. Follow the steps in this guide. Choose the right cables and equipment. Ensure proper placement for optimal sound. Test everything to catch any issues early. With these tips, you can enjoy a seamless audio experience.
Happy recording!
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How do I connect multiple studio monitors?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “To connect multiple studio monitors, use an audio interface with enough outputs. Connect each monitor to an output using balanced cables.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Do I need a specific audio interface?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Yes, you need an audio interface with multiple outputs. Ensure it supports balanced connections for better sound quality.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Can I use unbalanced cables?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Using unbalanced cables is not recommended. They are more prone to noise and interference. Always use balanced cables for better audio fidelity.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are balanced cables?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Balanced cables have three conductors: positive, negative, and ground. They help reduce noise and maintain signal integrity over long distances.” } } ] }
As an Amazon Associate, Cleanestor earns from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
