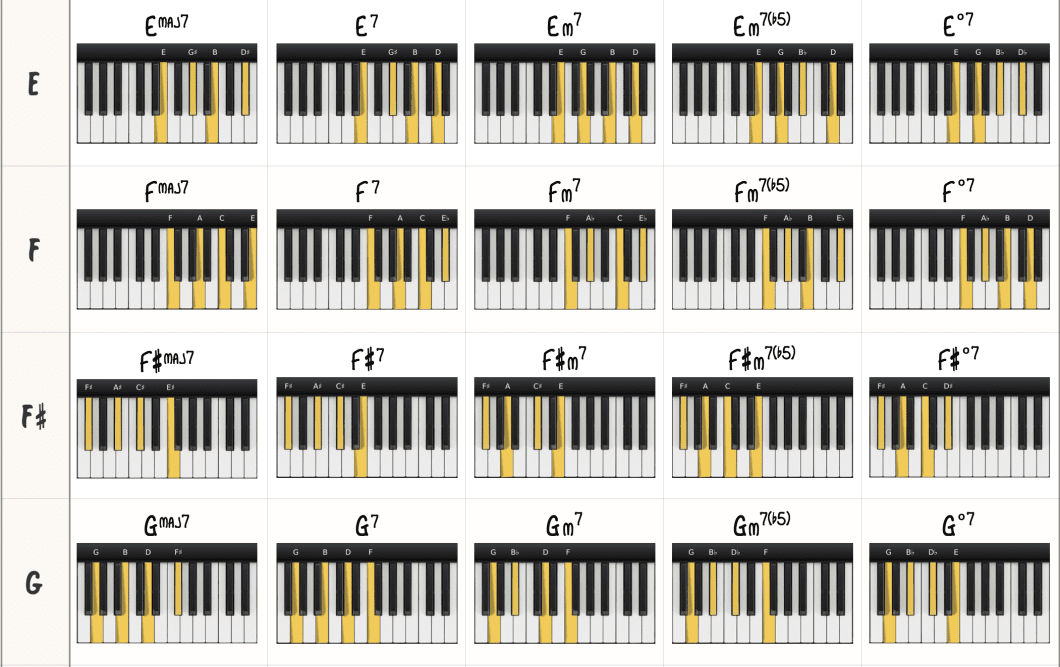
Jazz chords are complex harmonies often used in piano music to create a distinctively rich, improvisational sound. They typically include extended, altered, or added notes beyond traditional triads.
Understanding jazz chords on the piano can unlock a world of expressive musical possibilities, adding depth and color to your playing. These chords form the harmonic foundation of jazz music, characterized by swung rhythms, blue notes, and improvisation. Pianists use these chords to navigate the unique chord progressions that define jazz standards, and mastering them requires both theoretical knowledge and practical skill.
With a blend of major and minor sevenths, ninths, elevenths, and thirteenths, jazz chords infuse songs with a sense of sophistication and tonal nuance that’s iconic to the jazz genre. Whether you’re a budding pianist or a seasoned musician, delving into jazz chords can significantly broaden your musical repertoire and enhance your understanding of piano harmony.
Credit: pianowithjonny.com
The Essence Of Jazz Chords
Jazz chords mark the thrilling heart of jazz piano music. These chords create rich, complex sounds. They give jazz its distinctive flavor. Playing jazz chords means exploring a world of harmonic variety. Let’s unfold the vibrant layers that make up jazz chords on the piano.
Roots In African And European Music
Jazz chords owe their existence to a blend of cultures. African rhythms meet European harmonies in this fusion. This unique blend gave birth to jazz’s rhythmic drive and harmonic expressions. Let’s examine the key influences:
- African music provides the grooves and rhythmic patterns.
- European music brings chords and tonality into the mix.
Together, these elements intertwine to form the soulful basis of jazz chords.
Harmonic Complexity And Color
Jazz chords are famous for their intricate nature. They often have added notes like sevenths, ninths, or thirteenths. These notes expand the chord’s color palette.
| Chord Type | Notes | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Major 7th | 1-3-5-7 | Warm, full |
| Minor 7th | 1-♭3-5-♭7 | Smooth, cool |
| Dominant 7th | 1-3-5-♭7 | Bright, tense |
Such harmonic depth allows jazz pianists to express wide emotional ranges. Each chord choice paints a unique sonic picture.
Anatomy Of Jazz Chords
Exploring the inner workings of jazz chords on the piano reveals a world of harmonic complexity and beauty. These chords set the stage for jazz’s unique sound. Let’s delve into the anatomy of jazz chords to better understand how they form the backbone of this exceptional musical genre.
Basic Triads And Seventh Chords
Triads and seventh chords form the foundation of jazz harmony. A triad consists of three notes:
- The root, which gives the chord its name.
- The third, which determines if the chord is major or minor.
- The fifth, which is often perfect but sometimes altered.
Seventh chords add another layer:
- The seventh note can be major, minor, or diminished.
These chords create a fuller, more complex sound often heard in jazz.
Extensions And Alterations
Jazz musicians love to add extensions and alterations to their chords. Extensions include the:
- Ninth (a step above the octave)
- Eleventh (a fourth above the octave)
- Thirteenth (a sixth above the octave)
Alterations like #11 or b9 add tension and color to the chords.
Voicing Techniques
Voicings are how musicians spread out or arrange the notes of a chord:
- Open voicings have wide gaps between notes.
- Closed voicings have notes close to each other.
- Pianists use voicings to convey mood and expression in their playing.
Understanding these techniques helps us translate the language of jazz on the keyboard.
Common Jazz Chord Progressions
Exploring jazz piano opens a world filled with rich harmonic textures. Common jazz chord progressions form the backbone of this musical genre. They provide the framework for jazz improvisation and composition. Let’s dive into the essential progressions every aspiring jazz pianist should know.
The Ii-v-i Progression
The ii-V-I progression is the most iconic sequence in jazz. It consists of three basic chords:
- ii chord: A minor seventh chord based on the second note of the scale.
- V chord: A dominant seventh chord based on the fifth note of the scale.
- I chord: A major seventh chord based on the first note of the scale.
This sequence creates a sense of movement and resolution. It is the cornerstone of countless jazz standards.
Modal Interchange And Borrowed Chords
Jazz musicians often spice up progressions using modal interchange. They borrow chords from parallel scales to add color. Examples include:
- Minor iv chord in a major key.
- Major II chord in a minor key.
Borrowed chords surprise listeners and keep the music fresh and unpredictable.
Turnarounds And Cycle Of Fifths
Turnarounds lead the music back to the beginning of a section. They commonly use the cycle of fifths. This includes successive chords whose roots are a perfect fifth apart. Here’s the typical sequence:
- VII chord
- III chord
- VI chord
- II chord
- V chord
- I chord (Resolution)
This pattern creates a smooth flow through different chords and is a foundation in jazz harmony.
Credit: www.openstudiojazz.com
Chord Substitutions And Reharmonization
Chord Substitutions and Reharmonization in jazz piano open up a world of creativity. They let pianists turn simple tunes into rich, complex musical landscapes. These techniques are not just for the pros. Anyone can start using them with a bit of practice. Let’s dive into some exciting ways to jazz up those chords!
Tritone Substitutions
Tritone substitutions add spice to chord progressions. A tritone is three whole steps apart. In substitution, replace the original chord’s dominant with another. This new chord shares two notes with the original. It creates tension, leading smoothly to the next chord. Here’s an example:
- Original: Dmin7 – G7 – Cmaj7
- With Tritone Sub: Dmin7 – Db7 – Cmaj7
Backdoor Progressions
Backdoor progressions sneak into chord sequences subtly. Think of them as a backdoor into the usual resolution. For instance, in the key of C, instead of going from G7 to Cmaj7, slip in using a backdoor. The sequence transforms. Here’s how it looks:
- Approach chord (Fmin7)
- Backdoor dominant (Bb7)
- Target chord (Cmaj7)
Coltrane Changes
Coltrane Changes, named after the legend John Coltrane, rework chord progressions drastically. These changes cycle through keys separated by major thirds. This gives an excitingly rapid shift in harmony. The famous “Giant Steps” progression is the best example.
| Original Chords | Coltrane Changes |
|---|---|
| Cmaj7 | Emaj7 – D7 – Gmaj7 |
| Gmaj7 | Bmaj7 – Bb7 – Ebmaj7 |
Practical Application And Tips
Understanding the practical application and tips for playing jazz chords on the piano is key to mastering this musical art form. Jazz chords are rich and complex. They create sounds that evoke deep emotion and sophisticated musical textures. To navigate the world of jazz piano, use the following guidelines and strategies to enhance your playing skills.
Learning And Memorizing Jazz Standards
Jazz standards are classic tunes known in the jazz world. To play jazz effectively, it is essential to learn and memorize these pieces. Here’s how you can do it:
- Listen repeatedly to recordings of the standard you’re learning.
- Break down the piece into sections and practice each one.
- Create flashcards with chord symbols to quiz yourself.
- Practice with a metronome to internalize the tempo.
- Join jam sessions to play the standards in a live context.
Incorporating Rhythm And Groove
Rhythm and groove give jazz its characteristic swing. Here are tips to incorporate them into your playing:
- Start with a simple chord progression, playing with a steady beat.
- Focus on the timing of your left hand to maintain the groove.
- Use different articulation techniques, like staccato and legato.
- Experiment with syncopation by stressing off-beats.
- Practice with drum tracks or a metronome set to a swing rhythm.
Improvisation Over Complex Chords
Improvisation is a thrilling aspect of jazz piano. To improvise confidently over complex chords, consider these strategies:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Learn Scales | Master scales associated with each chord to find suitable notes. |
| Practice Arpeggios | Play chord tones in sequence to outline harmony. |
| Use Patterns | Start with fixed patterns and modify them as you get comfortable. |
| Embrace Rests | Silence can be powerful. Use it to add depth to your improvisation. |
| Record Yourself | Listen back and critique your improvisations to improve. |
Credit: ar.pinterest.com
Listening And Analysis
Understanding jazz chords on the piano takes more than just practice. It involves deep listening and analysis of the genre’s greats. By tuning into their music, aspiring pianists can unlock the mysteries of jazz harmonies. This process starts with study techniques like dissecting performances and using transcription as a learning tool.
Dissecting The Masters
Listen closely to your jazz piano heroes. Each chord they play tells a story. Think about the emotions these chords stir up. Is there a sense of tension? Maybe a feeling of release? To really get inside the music, follow these steps:
- Choose a recording of a jazz pianist you admire.
- Focus on a small section. Listen to it several times.
- Write down any chords that stand out to you.
- Look for patterns or techniques the artist uses.
This focused listening will help you understand not just what the masters play, but how they think and feel about the music they create.
Transcription As A Learning Tool
Transcribing solos and chord progressions by ear can be a game changer. It’s like learning to speak a new language the natural way—by listening and imitating. To start transcribing, consider these steps:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Listen to the piece. |
| 2 | Pause and repeat short sections. |
| 3 | Identify and write down each note. |
| 4 | Compare your transcription to the original. |
Patience is key in this process. Attempt easier pieces first, then gradually move up to complex ones. The reward? A profound understanding of jazz chords and an improved ability to play them on the piano.
Can Different Types of Pianos Affect how Jazz Chords are Played?
When playing jazz chords, the type of piano used can make a difference in the sound and feel of the music. Some pianos, like the classic grand piano, offer a rich and resonant tone that is well-suited for jazz music. Therefore, choosing the best piano for jazz music is crucial for achieving the desired sound.
Are Jazz Chords Used in Piano Music and How Do They Relate to Other Piano Chords?
Jazz chords add depth and complexity to piano music, often creating rich textures that differ from traditional major and minor chords. By using extended harmonies and altered tones, musicians can explore the distance between piano chords effectively, enhancing their compositions and improvisations while bridging various musical genres.
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Are Jazz Chords Piano
What Are The Basic Jazz Chords?
Basic jazz chords include major 7th, minor 7th, dominant 7th, and half-diminished chords. Mastery of these shapes provides a solid foundation for playing jazz progressions.
What Defines A Jazz Chord?
A jazz chord typically includes extended harmonies like 7ths, 9ths, 11ths, and 13ths. These chords create rich, complex sounds characteristic of jazz music.
What Is The Difference Between Jazz Chords And Regular Chords?
Jazz chords often incorporate extensions and alterations, like 7ths, 9ths, and sharp 11ths, creating more complex harmonies. Regular chords typically consist of triads or basic seventh chords, yielding simpler sounds.
What Is The Best Chord Progression For Jazz Piano?
The best chord progression for jazz piano often involves the 2-5-1 sequence. Known as a ‘ii-V-I’, this fundamental progression underpins numerous jazz standards and showcases improvisational skills effectively.
Conclusion
Mastering jazz chords on the piano unlocks a universe of harmonic richness, vital for any aspiring jazz musician. Delve into these chord structures, practice diligently, and infuse your playing with the unique flavor that defines jazz. Embrace the journey, and let your creativity soar on the keys.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are the basic jazz chords?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Basic jazz chords include major 7th, minor 7th, dominant 7th, and half-diminished chords. Mastery of these shapes provides a solid foundation for playing jazz progressions.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What defines a jazz chord?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “A jazz chord typically includes extended harmonies like 7ths, 9ths, 11ths, and 13ths. These chords create rich, complex sounds characteristic of jazz music.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the difference between jazz chords and regular chords?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Jazz chords often incorporate extensions and alterations, like 7ths, 9ths, and sharp 11ths, creating more complex harmonies. Regular chords typically consist of triads or basic seventh chords, yielding simpler sounds.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the best chord progression for jazz piano?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “The best chord progression for jazz piano often involves the 2-5-1 sequence. Known as a ‘ii-V-I’, this fundamental progression underpins numerous jazz standards and showcases improvisational skills effectively.” } } ] }As an Amazon Associate, Cleanestor earns from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
