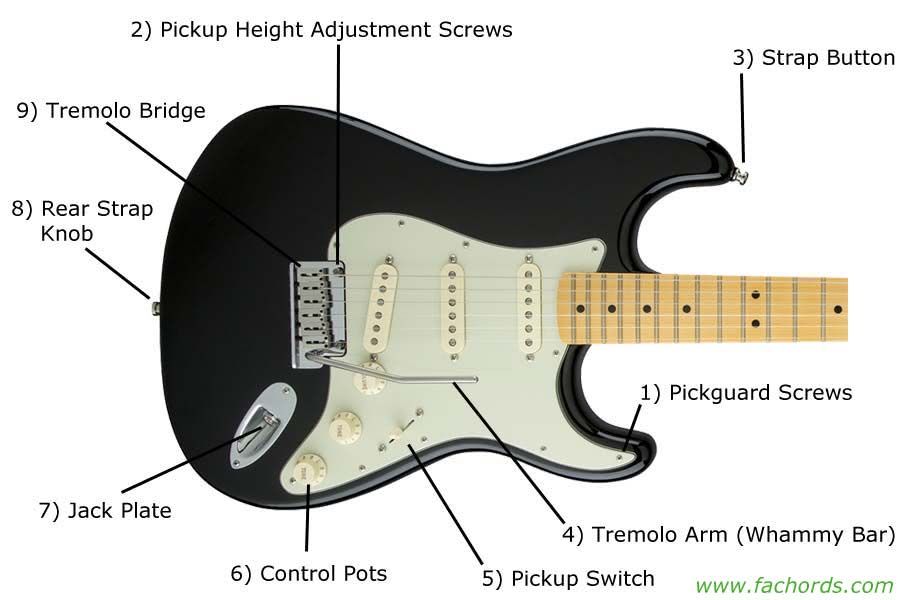
The main parts of an electric guitar are the body, neck, headstock, pickups, bridge, and tuning pegs. The fretboard, strings, and control knobs are also key components.
Understanding the parts of an electric guitar can enhance your appreciation of its design and function. This iconic instrument is more than a piece of musical art; it’s an intricate assembly of various elements that work together to produce rich, electrifying sounds.
Each part plays a vital role, from the body that houses the electronics to the neck that supports the fretboard for note variation. Players and enthusiasts alike delve into the specifics of each component, seeking the perfect blend of aesthetics and sound quality. Knowledge of an electric guitar’s anatomy is fundamental for anyone wishing to master the instrument or maintain it in top condition. With precision engineering and a touch of personal flair, electric guitars continue to be a centerpiece in music genres across the board.
Credit: www.fachords.com
Introduction To The Electric Guitar
Welcome to the electrifying world of music, where the electric guitar stands as a central pillar of modern sound. A marvel of engineering and creativity, the electric guitar revolutionized music, giving artists the power to explore new sonic horizons. Let’s delve into the anatomy of this iconic instrument and trace its journey through history.
Defining The Electric Guitar
An electric guitar is a stringed musical instrument, typically crafted with a solid, semi-hollow, or hollow body, and played by plucking or strumming the strings, which are magnetically picked up by devices known as pickups. These vibrations transform into electric signals, amplified to produce the rich, versatile tones that characterize genres from rock and jazz to blues and beyond. Key components include:
- Body: The main part of the guitar that houses pickups and electronics.
- Neck: Attached to the body, it holds the fretboard, frets, headstock, and tuners.
- Fretboard: A flat surface on the neck, lined with frets, where fingers are placed to create notes.
- Pickups: Devices that capture string vibrations and convert them into electrical signals.
- Bridge: Anchors the strings and can affect their vibration length and pitch.
- Tuners: Located on the headstock, they adjust the pitch of each string.
- Controls: Knobs and switches that modify volume and tone or select different pickups.
Historical Evolution Of Electric Guitar Design
The electric guitar’s history is a tapestry woven with innovation and artistic expression. The journey began in the early 20th century when musicians sought greater volume to compete with other instruments. Early pioneers experimented with magnetic pickups, and by the 1930s, the first commercially available electric guitars emerged. Key milestones include:
- The 1931 introduction of the Rickenbacker ‘Frying Pan,’ the first electric lap steel guitar.
- The invention of the Solid-body electric guitar by Les Paul in the 1940s, paving the way for louder, clearer sounds without the feedback issues of hollow bodies.
- The 1950s and 1960s, when brands like Fender and Gibson introduced models like the Stratocaster and Les Paul, which became the gold standard for electric guitars.
- The continual innovation in guitar electronics, materials, and design that shapes the instruments in use today.
Each design change reflected the evolving needs of musicians and contributed to the electric guitar’s standing as a versatile and enduring icon of music.
Anatomy Of The Electric Guitar: A Component Overview
Embark on a sonic adventure as we dissect the electric guitar, an instrument celebrated for its versatility and rich tonal textures. Whether you’re a gripping guitarist or an avid aficionado, understanding each part’s role can amplify your appreciation. Let’s unravel the mystique of the electric guitar, piece by piece.
The Body: Material And Design Variations
The body isn’t just the guitar’s chassis; it’s the heart of its visual appeal and sonic prowess. Body materials typically include woods such as alder, mahogany, or maple, each contributing distinct resonance characteristics. Meanwhile, the design varies from the iconic contours of a Stratocaster to the solid heft of a Les Paul. These variations affect weight, balance, and ultimately, the character of the sound produced.
The Neck: Fretboard, Headstock, And Truss Rod
Connecting to the body, the neck acts as a critical conduit for both player interaction and tonality. The fretboard, adorned with frets for pitch precision, often boasts woods like rosewood or ebony. The headstock, crowned with tuning machines, governs string tension while the truss rod, hidden within the neck, maintains curvature against string tension and environmental adjustments.
Pickups And Electronics: Types And Tonal Impact
- Single-coils: Known for their bright and crisp sound, often found in Fender guitars.
- Humbuckers: Double-coil pickups that cancel hum and deliver a warmer, fuller tone, commonly seen in Gibson models.
- Active pickups: Powered by a battery, these offer higher output and are beloved in genres demanding assertive sounds.
The guitar’s voice is sculpted here, harnessed by volume and tone controls, alongside switches that select or combine pickup outputs.
Bridge And Tailpiece: Function And Varieties
The bridge not only anchors strings but also plays a crucial role in sustain and intonation. Tailpieces may be integrated or separate and come in styles like the whammy bar-equipped tremolo or the steadfast fixed bridge. Whether it’s to create soul-stirring vibratos or provide rock-solid tuning stability, these components are instrumental in defining playability.
Tuning Machines: Ensuring Pitch Stability
Above all, the precision of tuning machines holds the sanctity of your sound. These geared mechanisms, also known as tuners or pegs, uphold the strings’ pitch with steadfast tension. Their quality can mean the difference between seamless play and frequent tuning pauses, ensuring artists can focus on the music, not the mechanics.
Understanding Guitar Hardware And Accessories
An electric guitar, while remarkable for its musical potential, is also a marvel of engineering. From the smooth turn of a knob to the snug fit of a strap button, every piece of guitar hardware and accessories plays a crucial role in the instrument’s function and playability. Delving into these components not only satisfies our curiosity but also enhances our understanding and appreciation of the instrument we love. Let’s explore the essential hardware and accessories that contribute to our electric guitar experience.
Knobs, Switches, And Pots: Controlling The Sound
Guitar electronics might seem like arcane wizardry, but they’re surprisingly straightforward once you decipher their functions. Knobs attached to potentiometers, or pots for short, let players adjust volume and tone, shaping the sound to their liking. Manipulating these allows for a spectrum of tones, from deep, resonant bass to piercing treble sounds.
Switches play a critical part in electric guitar versatility. These components are critical for selecting different pickup configurations, offering an array of sounds that can match various music genres and playing styles.
Nut And Saddles: Their Role In Intonation And Action
The nut and saddles provide foundational support to a guitar’s strings, sitting at the headstock and bridge, respectively. They are vital in maintaining proper intonation and action. An accurately slotted nut and precisely shaped saddles ensure that the strings are at the correct height from the fretboard and that they maintain pitch across the entire length of the neck.
Strap Buttons And Pickguards: Convenience And Protection
Strap buttons are the unsung heroes of guitar hardware, securing the strap to the instrument for easy handling during performances. Without these, the majestic stance of a guitarist would falter, potentially leading to mishaps. In conjunction, pickguards shield the guitar’s finish from the enthusiastic strums and picks that come with impassioned playing. They are functional guardians against wear and tear, contributing to the guitar’s longevity.
Output Jack: Connecting The Guitar To An Amplifier
The output jack is the portal through which the magic of the electric guitar enters the broader world of music. As the bridge between guitar and amplifier, this small component carries the intricate electric signals picked up from the strings and transfers them to your amp, where they’re transformed into the sound that fills rooms and hearts alike. A stable and clean jack connection is crucial for a clear and uninterrupted signal flow.

Credit: how-to-play-electric-guitar.net
Customizing And Upgrading Electric Guitar Parts
Customizing and Upgrading Electric Guitar Parts is an exciting endeavor for any musician looking to create a more personalized and high-performing instrument. The electric guitar’s modular nature allows for extensive customization, ensuring each player can find the perfect combination of parts to match their playing style and aesthetic preferences. Whether seeking improved playability, enhanced tone, or a new look, there are numerous avenues to explore. Let’s dive into some of the most popular ways to upgrade your electric guitar.
Popular Modifications For Improved Playability
Guitarists often prioritize playability above all else. Achieving the ideal setup can transform a challenging instrument into a dream guitar. Essential modifications that greatly impact playability include:
- Fretwork: Levelling, crowning, and polishing frets to ensure smooth and buzz-free playing.
- Nut replacement: Installing a high-quality nut crafted from bone, graphite, or synthetic materials to improve tuning stability.
- Action adjustment: Customizing string height for optimal finger movement and comfort.
- Neck profile reshaping: Modifying the neck’s contour to fit the player’s hand preferentially.
Upgrading Pickups And Electronics For Tone Enhancement
The heart of an electric guitar’s sound lies in its pickups and electronics. Upgrades here can result in dramatic changes to the guitar’s tone:
- Replacing stock pickups with high-quality aftermarket models to achieve desired sound characteristics.
- Installing coil-tap or coil-split features to provide additional tonal options.
- Upgrading potentiometers and switches for more precise control over volume and tone.
- Adding a preamp or active circuitry for enhanced signal strength and tonal shaping.
Replacing Hardware For Aesthetics And Durability
Hardware upgrades not only improve the look of your guitar but can also contribute to its functionality and durability. Consider these changes for a fresh look and a more resilient setup:
| Hardware Component | Purpose | Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Tuning Machines | Enhance tuning stability and provide a smoother tuning experience. | Options include chrome, black nickel, gold, and locking tuners. |
| Bridge | Improve sustain and intonation accuracy. | Varieties include fixed bridges, tremolos, and those made of titanium or brass. |
| Control Knobs & Switch Tips | Revitalize the guitar’s aesthetic and touchpoints. | Custom colors and designs to match your style. |
| Strap Buttons | Ensure secure strap attachment, possibly with locking systems. | Durable metals or even customized shapes and themes. |
Maintaining Your Electric Guitar’s Parts
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your electric guitar involves regular maintenance of its various components. From the shiny tuners down to the sturdy input jack, each part requires care and attention. A well-maintained guitar not only stays in tune and sounds better, but it also retains its value over time. In this section, we’ll look at how to keep your cherished instrument in prime condition, troubleshoot common problems, and recognize when professional help is necessary.
Regular Cleaning And Care For Longevity
Regular cleaning is pivotal for the longevity of any electric guitar. Dust, grime, and fingerprints can accumulate, not just on the guitar’s body, but also in the hard-to-reach areas around the bridge, pickups, and tuning pegs.
- Body and neck: Use a soft, dry cloth for daily dusting and a damp cloth followed by a dry one for weekly cleaning.
- Fretboard: Clean it every few months with special fretboard oil to prevent it from drying out and cracking.
- Strings: Wipe them down with a clean cloth after every use to remove oils and prolong their life.
- Hardware: Polish the metal parts gently with suitable cleaners to avoid tarnishing.
Troubleshooting Common Electric Guitar Issues
Troubles with electric guitars are inevitable, but many can be resolved at home. Recognize common issues and take action promptly to fix them.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Quick Fix |
|---|---|---|
| String Buzz | Loose hardware or uneven frets | Tighten all screws and check fret level |
| Electronics Noise | Dirty potentiometers or jacks | Clean with contact cleaner spray |
| Intonation Problems | Improperly set bridge or old strings | Adjust bridge and replace strings |
When To Seek Professional Maintenance Or Repair
While regular cleaning and troubleshooting can be routinely handled at home, certain signs indicate the need for professional maintenance or repair:
- When intonation adjustments do not fix tuning issues,
- If there’s persistent fret buzz across multiple frets even after checking for loose hardware,
- In case of electronic failures such as non-working pickups or knobs that crackle despite cleaning,
- Or if structural damage to the neck or body is visible.
It’s best to trust experienced technicians with the specialized tools and expertise to address these complex issues and ensure your guitar returns to its best playability and sound.
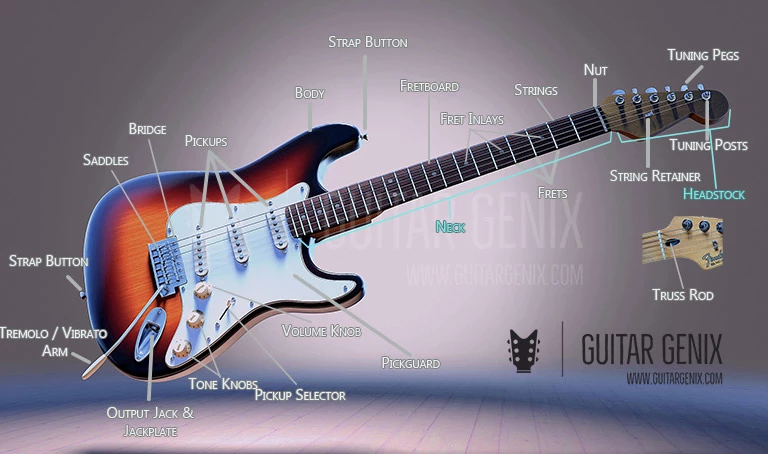

Credit: www.guitargenix.com
How Do Electric Guitar Amplifiers Enhance the Sound of Different Parts of an Electric Guitar?
Understanding electric guitar amplifiers is essential for any player looking to enhance their sound. These devices shape the tonal quality, emphasizing the nuances of different pickups and effects. By manipulating gain, tone, and volume settings, musicians can tailor their sound, bringing out the character of each chord and note in stunning detail.
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Are The Parts Of An Electric Guitar
What Are The Most Important Parts Of The Electric Guitar?
The most crucial parts of an electric guitar are the body, neck, fretboard, pickups, tuners, bridge, and strings. Each component plays a vital role in sound production and playability.
What Makes Up An Electric Guitar?
An electric guitar consists of a body, neck, strings, pickups, a bridge, and tuning pegs. Pickups convert string vibrations into electrical signals that amplify through a speaker.
What Are The Components Of A Guitar?
A guitar comprises six main components: the headstock, tuners, neck, fretboard, body, and strings. Each part plays a crucial role in producing sound.
What Is The Metal Thing On An Electric Guitar?
The metal thing on an electric guitar is likely a bridge, pickup selector, tuning machine, or fret, essential for sound production and pitch adjustment.
Conclusion
Understanding the various parts of an electric guitar is essential for players and enthusiasts alike. From the headstock to the tailpiece, each component plays a critical role in shaping the instrument’s sound and playability. Remember, every piece matters whether you’re performing a soulful solo or mastering chords.
Embrace the symphony of electronics and craftsmanship that makes your electric guitar truly sing.
