A drum produces a distinctive sound. It can vary based on the type of drum.
Drums are one of the oldest musical instruments known to humanity. They have been used in various cultures for centuries. The sound a drum makes depends on its size, shape, and the material of its drumhead. A snare drum, for example, creates a sharp, crisp sound.
In contrast, a bass drum produces a deep, resonant boom. Different techniques, such as striking the drum with sticks or hands, can also affect the sound. Understanding the unique sounds of different drums can enhance your appreciation of music. In this blog post, we will explore the diverse sounds that various drums make and what influences these sounds. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of drumming!

Credit: drummagazine.com
Introduction To Drum Sounds
The drum is one of the oldest musical instruments. Its unique sounds have fascinated people for centuries. Drums are found in nearly every culture around the world. Understanding drum sounds can enhance your appreciation of music.
Basic Drum Types
Drums come in various shapes and sizes. Each type produces a different sound. The bass drum is large and produces a deep, resonant sound. The snare drum has a sharp, crisp sound. Tom-toms are medium-sized drums with a round, full tone. Each drum type adds its unique voice to music.
Cultural Significance
Drums hold special meaning in many cultures. In Africa, drums are used in ceremonies and communication. Native American tribes use drums in spiritual rituals. In Asia, drums accompany traditional dances and celebrations. These cultural connections add depth to the sound of drums.
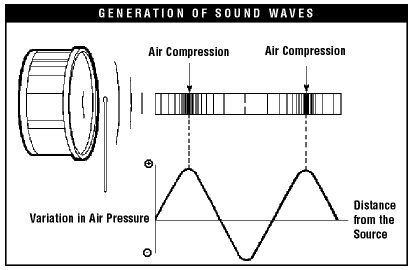
Credit: www.ccohs.ca
Elements Of Drum Sounds
The elements of drum sounds are crucial for any drummer. They shape the music and create a unique experience. Understanding these elements helps in crafting the perfect beat. Two primary factors are pitch and tone and volume and intensity.
Pitch And Tone
Pitch refers to how high or low a drum sound is. Different drums produce different pitches. For example, a snare drum has a higher pitch than a bass drum.
Tone describes the quality of the drum sound. It includes the brightness, warmth, and fullness of the sound. Adjusting the drum head tension can change the tone. A tighter head gives a brighter tone. A looser head gives a warmer tone.
| Drum Type | Pitch | Tone |
|---|---|---|
| Snare Drum | High | Bright |
| Bass Drum | Low | Warm |
| Tom-Tom | Medium | Full |
Volume And Intensity
Volume is the loudness of the drum sound. It depends on how hard you hit the drum. A soft hit produces a low volume. A hard hit produces a high volume.
Intensity is the energy of the drum sound. It adds emotion and dynamics to the music. Intensity can be varied within a performance to create a sense of movement.
- Soft hits give a gentle sound.
- Hard hits give a powerful sound.
- Consistent hits maintain a steady intensity.
- Varied hits create dynamic intensity.
Mastering the elements of drum sounds is essential for every drummer. It enhances the overall musical experience.
Drum Materials And Their Impact
Different drum materials create unique sounds. Wood drums produce warm, deep tones. Metal drums offer bright, sharp sounds. Plastic drums give a modern, versatile sound.
Drums create diverse sounds. The material used impacts the sound quality. Different materials produce distinct tones.Wood Vs. Metal
Wooden drums produce warm, rich sounds. Maple, birch, and mahogany are popular choices. Maple drums have a balanced tone. Birch drums offer bright sounds. Mahogany drums produce deep, resonant tones. Metal drums have a brighter, sharper sound. Aluminum, brass, and steel are common. Aluminum drums create a dry, crisp tone. Brass drums produce a warm, full-bodied sound. Steel drums have a loud, cutting tone.Synthetic Materials
Synthetic materials offer unique tones. Fiberglass, acrylic, and carbon fiber are examples. Fiberglass drums produce a focused, punchy sound. Acrylic drums have a bright, loud tone. Carbon fiber drums offer a balanced, versatile sound. The choice of material affects the drum’s sound. Each material offers a unique tone. Choose based on the desired sound. “`
Credit: www.soundonsound.com
Drumhead Types And Effects
The sound of a drum is greatly influenced by the type of drumhead used. Drumheads come in various types, each affecting the sound in different ways. Understanding these differences can help you achieve the desired sound for your music.
Single Vs. Double Ply
Drumheads can be either single ply or double ply. A single ply drumhead consists of one layer of material. This makes it more sensitive and responsive, producing a brighter sound. Single ply heads are often used for jazz or lighter playing styles.
On the other hand, a double ply drumhead is made of two layers of material. This makes it more durable and capable of handling heavier playing. Double ply heads produce a deeper, more focused sound, making them ideal for rock or heavy metal genres.
| Type | Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Single Ply | Bright sound, sensitive | Jazz, light playing |
| Double Ply | Deep sound, durable | Rock, heavy metal |
Coated Vs. Clear
Drumheads also come in coated or clear versions. A coated drumhead has a textured surface. This texture adds warmth to the sound and provides better stick control. Coated heads are popular for genres like jazz and blues.
A clear drumhead lacks this coating, resulting in a more open and bright sound. Clear heads are often used in rock and pop music due to their clarity and attack.
| Type | Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Coated | Warm sound, better stick control | Jazz, blues |
| Clear | Open sound, bright | Rock, pop |
Playing Techniques
Understanding the playing techniques is vital for creating different drum sounds. Various methods produce unique tones and dynamics. This section covers two major techniques: stick control and hand drumming.
Stick Control
Stick control is a fundamental skill for drummers. Using sticks allows for precise and powerful strikes on the drum surface.
- Grip: Hold the sticks firmly but not too tight. This helps in controlling the bounce.
- Wrist Movement: Use your wrists to control the stick movement. Avoid using your arms too much.
- Practice Drills: Regular practice improves your stick control. Try exercises like single strokes and double strokes.
Stick control affects the drum’s volume and tone. Proper technique makes your drumming clear and dynamic. Below is a simple table for stick control exercises:
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Single Strokes | Alternate hits with each stick. |
| Double Strokes | Two hits per stick before switching. |
| Paradiddles | Play RLRR LRLL patterns. |
Hand Drumming
Hand drumming involves using your hands to strike the drum. This method creates a more natural and warm sound.
- Open Tone: Strike the drum near the edge using your fingers and palm. This creates a resonant sound.
- Slap: Hit the drum sharply with your fingers. This produces a sharp, popping sound.
- Bass Tone: Strike the drum center with your palm. This creates a deep, bass sound.
Hand drumming allows for expressive playing. Each type of hit creates a different sound. Practice these techniques to improve your hand drumming skills.
Tuning And Its Influence
Drums produce a wide range of sounds. The secret? Tuning. Proper tuning changes the drum’s tone, pitch, and resonance. It creates the desired sound for different music genres. Let’s delve into how tuning impacts drum sounds.
Tension Adjustment
Tension adjustment is crucial. Tightening or loosening the drumhead affects the pitch. A tighter drumhead gives a higher pitch. A looser drumhead gives a lower pitch. This adjustment is done by turning the drum’s tension rods. Here’s a quick guide:
- High Tension: Higher pitch, sharper sound.
- Low Tension: Lower pitch, deeper sound.
Drummers often use a drum key for precise adjustments. Ensuring even tension around the drumhead is key. Uneven tension can cause unwanted overtones.
Resonance Control
Resonance is the drum’s ability to sustain sound. Controlling resonance affects the drum’s sustain and tone. Resonance can be managed through several methods:
| Method | Effect |
|---|---|
| Moongel | Reduces unwanted overtones. |
| O-Rings | Shortens sustain. |
| Internal Muffling | Softens the sound. |
Each method offers unique benefits. Moongel pads are popular for their ease of use. O-rings are great for achieving a controlled sound. Internal muffling is often found in bass drums.
Tuning and resonance control are essential for drummers. They shape the drum’s sound and suit different music styles. Experiment with these techniques to find your perfect drum sound.
Common Drum Sounds
The world of drum sounds is vast and varied. Each drum in a drum set has a unique sound. These sounds create the rhythm and feel of a song. Let’s explore some common drum sounds.
Snare Drum Snap
The snare drum is the backbone of the drum set. Its sound is sharp and crisp. The snap of the snare drum cuts through the mix. This makes it a key component in many genres.
Snare drum sounds can be described as:
- Bright
- Crackling
- Sharp
Drummers often place the snare drum in the center of their setup. They use sticks to hit the drum head and the metal wires underneath. This creates the distinctive snap sound.
Bass Drum Thump
The bass drum provides the deep, thumping sound in a drum set. It is also called the kick drum. Drummers use a foot pedal to play the bass drum. This allows for a powerful and steady beat.
Bass drum sounds are often described as:
- Deep
- Resonant
- Thudding
The bass drum is usually the largest drum in the set. Its sound is felt as much as it is heard. This makes it essential for the rhythm section of any band.
Recording Drum Sounds
Recording drum sounds requires careful attention to detail. The right techniques make a huge difference. The way you place microphones and mix sounds can either enhance or ruin your recording. Let’s dive into some key aspects.
Microphone Placement
Mic placement is crucial for capturing a drum’s true sound. Each drum in the kit has its own unique voice. Proper mic placement ensures these voices blend harmoniously.
Here are some tips for optimal microphone placement:
- Snare Drum: Position the mic about 2 inches above the rim. Aim it at the center of the drum head.
- Bass Drum: Place a mic inside the drum, near the beater. This captures the punchy low end.
- Tom-Toms: Angle the mic towards the center, about 2 inches above the drum head.
- Hi-Hat: Position the mic 3-4 inches above, aiming at the edge of the top cymbal.
- Overhead Mics: Place them about 3 feet above the kit. This captures the overall sound and ambiance.
Sound Mixing Tips
Once you have your recordings, mixing is the next step. Proper mixing can make your drums sound polished and professional.
Here are some sound mixing tips:
- Balance Levels: Ensure each drum is at the right volume. The snare and bass drum are usually more prominent.
- EQ Settings: Use EQ to carve out space for each drum. Cut unwanted frequencies to avoid muddiness.
- Compression: Apply compression to control dynamics. This makes the drums sound more consistent.
- Reverb: Add reverb to give the drums a sense of space. Be cautious not to overdo it.
- Panning: Pan drums to mimic a live setup. For example, hi-hats to the left, floor toms to the right.
By following these tips, you can create a drum sound that is both clear and dynamic. Happy recording!
Does Upswinging Include the Sound of Drums?
Exploring upswinging and percussion reveals a fascinating connection between rhythm and emotional elevation. The sound of drums can amplify the experience, driving energy and movement. As notes rise, they intertwine with the beat, creating a vibrant tapestry of sound that inspires both dancers and listeners to revel in the uplifting atmosphere.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Sound Does A Drum Make?
A drum produces a deep, resonant, and rhythmic sound. The tone can vary based on the drum type and playing technique.
How Do Different Drums Sound?
Different drums create varied sounds. For example, a snare drum is sharp and crisp, while a bass drum is deep and booming.
What Factors Affect Drum Sounds?
Drum sounds are influenced by drum size, material, tuning, and the type of drumsticks used.
Why Do Drums Sound Different?
Drums sound different due to their construction materials, size, and the way they are played or struck.
Conclusion
Drums create unique and captivating sounds. They can be loud, soft, or rhythmic. Each beat tells a story. Drums are versatile and fit into many music genres. Understanding drum sounds enhances music appreciation. Next time you hear a drum, listen closely.
Notice the variations in sound. Feel the rhythm. Enjoy the experience. Drums are more than instruments; they are storytellers. So, keep exploring different drum sounds. Let the beats inspire you.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What sound does a drum make?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “A drum produces a deep, resonant, and rhythmic sound. The tone can vary based on the drum type and playing technique.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How do different drums sound?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Different drums create varied sounds. For example, a snare drum is sharp and crisp, while a bass drum is deep and booming.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What factors affect drum sounds?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Drum sounds are influenced by drum size, material, tuning, and the type of drumsticks used.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Why do drums sound different?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Drums sound different due to their construction materials, size, and the way they are played or struck.” } } ] }As an Amazon Associate, Cleanestor earns from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.

