A line input on an audio interface is a connection point. It allows audio signals from other devices to be fed into the interface.
This is crucial for recording and mixing audio. Understanding a line input is vital for anyone working with audio. It helps connect various devices like keyboards, mixers, and drum machines to your audio interface. These inputs handle line-level signals, which are stronger than microphone signals.
This ensures a clean, clear sound. Knowing how to use line inputs can improve your audio projects. It makes the process of recording and mixing more efficient. In this post, we will explore what a line input is and why it matters in audio production. Stay tuned to learn more about maximizing your audio interface capabilities.
Introduction To Line Inputs
Line inputs are essential components in audio interfaces. They allow you to connect various audio devices. This section will explain what a line input is and why it is important.
Definition
A line input is an input on an audio interface. It is designed to receive audio signals from external sources. These sources can include instruments, mixers, and other audio equipment. Line inputs usually handle signals at line level. This is a standard audio signal level in professional audio equipment.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Line Input | Receives audio signals from external devices. |
| Mic Input | Designed for microphone signals, usually at lower levels. |
| Instrument Input | For directly connecting instruments like guitars. |
Importance In Audio Interfaces
Line inputs play a crucial role in audio interfaces. They ensure the compatibility of various audio devices. Without line inputs, connecting different audio sources would be challenging.
- Line inputs provide a clean signal path.
- They help maintain audio quality.
- They allow for flexibility in audio setups.
Most modern audio interfaces include multiple line inputs. This allows users to connect several devices simultaneously. For example, you can connect a synthesizer, a drum machine, and a mixer all at once.
Understanding line inputs helps you make better use of your audio interface. It ensures your audio setup is efficient and versatile.
Types Of Line Inputs
Understanding the types of line inputs on an audio interface is crucial for any audio enthusiast. These inputs are key to ensuring high-quality sound. There are two main types: balanced and unbalanced line inputs. Each has its unique characteristics and uses. Let’s explore each type in detail.
Balanced Line Inputs
Balanced line inputs are designed to reduce noise and interference. They use three wires: positive, negative, and ground. This setup helps in canceling out unwanted noise.
Balanced line inputs are ideal for long cable runs. They maintain audio quality over distances. Common connectors for balanced inputs include XLR and TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve). These connectors are often used in professional audio equipment.
Example:
| Connector Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| XLR | Microphones, professional audio gear |
| TRS | Instruments, balanced audio connections |
Unbalanced Line Inputs
Unbalanced line inputs are simpler in design. They use two wires: signal and ground. This makes them more susceptible to noise and interference.
Unbalanced inputs are suitable for short cable runs. They are often found in consumer audio equipment. Common connectors include TS (Tip-Sleeve) and RCA. These are widely used in home audio systems.
Example:
| Connector Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| TS | Guitars, short cable runs |
| RCA | Home audio systems, consumer electronics |
Choosing the right type of line input depends on your needs. For professional setups, balanced inputs are the way to go. For home audio, unbalanced inputs are often sufficient.
How Line Inputs Work
Understanding how line inputs work on an audio interface can help you get the best sound quality. Line inputs are essential for connecting external audio equipment to your interface. They play a crucial role in the recording and mixing process. Let’s delve into the details of how line inputs function.
Signal Flow
The signal flow is the path the audio signal takes from the source to the output. In a line input, the signal flow starts from your external device, like a keyboard or mixer. It then travels through a cable to the audio interface.
Once the signal reaches the interface, it enters the line input stage. The line input stage is designed to handle signals at a higher level than microphone inputs. This ensures the signal remains clear and strong.
Conversion Process
After the signal enters the line input, it undergoes the conversion process. This process converts the analog signal into a digital signal. The digital signal can then be processed by your computer or recording software.
The conversion process involves two main steps:
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC)
- Digital Processing
During ADC, the analog signal is sampled at a high rate. This creates a digital representation of the original sound. The digital processing stage then allows you to edit, mix, and refine the audio.
| Stage | Function |
|---|---|
| Signal Flow | Transfers audio signal from source to interface |
| Conversion Process | Converts analog signal to digital for processing |
Understanding these stages helps in achieving the best sound quality. Proper use of line inputs ensures your recordings are clear and professional.
Credit: productionden.com
Common Uses Of Line Inputs
Line inputs on an audio interface are crucial for many applications. They provide a way to connect various devices and instruments. This section explores common uses of line inputs.
Connecting Instruments
Musicians often use line inputs to connect their instruments. Keyboards, synthesizers, and electric guitars are common examples. This allows for clear, direct sound capture. Line inputs ensure the audio signal remains strong and clean. They are essential for recording high-quality sound.
Connecting External Devices
Line inputs are also used to connect external devices. These include mixers, CD players, and drum machines. Connecting these devices through line inputs allows seamless integration. It enhances the overall sound quality and workflow. This makes line inputs versatile and essential in many setups.
Differences Between Line Inputs And Other Inputs
Understanding the differences between line inputs and other inputs on an audio interface is essential for achieving the best sound quality. Knowing the right input ensures you get a clean and clear signal. Let’s dive into the differences between line inputs and other common inputs.
Line Vs. Mic Inputs
Mic inputs are designed for microphones. They have a lower impedance and higher sensitivity. This means they can pick up faint sounds with ease. They also often come with phantom power, which is necessary for condenser microphones.
In contrast, line inputs are for devices like keyboards, mixers, and audio players. They handle stronger signals without needing amplification. Using a mic input for a line-level device can cause distortion.
Line Vs. Instrument Inputs
Instrument inputs are made for electric guitars and basses. They have a higher impedance than mic inputs. This ensures that the signal from the guitar or bass is clear and strong. It is crucial to use an instrument input for these devices to avoid a weak or noisy signal.
On the other hand, line inputs are not suited for guitars or basses. They do not have the right impedance or sensitivity. Plugging a guitar into a line input can result in a poor sound quality.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Input Type | Impedance | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Mic Input | Low | Microphones |
| Instrument Input | High | Guitars/Basses |
| Line Input | Medium | Keyboards/Mixers |
Choosing the right input is crucial for sound quality. Always match the device with the correct input type to avoid issues.

Credit: www.soundonsound.com
Advantages Of Using Line Inputs
Line inputs on an audio interface offer various benefits for audio enthusiasts and professionals. These inputs can significantly enhance the overall sound experience. Below are some key advantages of using line inputs.
Audio Quality
Line inputs deliver superior audio quality. They provide a cleaner and more direct signal path. This minimizes the need for extra amplification stages. The result is a more faithful reproduction of the original sound.
Using line inputs helps in preserving the integrity of the audio signal. This ensures that the sound captured is as accurate and true-to-life as possible. Musicians and sound engineers can achieve a more natural and rich sound quality.
Noise Reduction
Line inputs are effective in reducing noise in audio recordings. They are less susceptible to interference from external sources. This is because they operate at a higher signal level than mic inputs. The higher signal levels help in maintaining a cleaner and clearer sound.
Utilizing line inputs can significantly lower the chances of unwanted noise. This is especially true in complex audio setups. The reduced noise floor leads to a more professional and polished audio output.
In summary, the advantages of using line inputs include enhanced audio quality and effective noise reduction. These benefits make line inputs an essential feature for anyone serious about audio production.
Choosing The Right Line Input
Choosing the right line input for your audio interface can be crucial. It ensures the best sound quality and performance. But how do you know which one is right for you? Let’s break it down into key factors. These include compatibility and technical specifications.
Compatibility
First, check if the line input is compatible with your gear. Your instruments, microphones, or other audio sources. Different devices have different output levels. So, make sure the line input can handle it.
Look at the connectors. Are they XLR, TRS, or RCA? Match them with your equipment. This ensures you can plug in without any issues.
Technical Specifications
Next, consider the technical specifications. Look at the input impedance. It should match your equipment’s output impedance. This affects the sound quality.
Check the frequency response. A wider range captures more detail. This helps in achieving a richer sound. Also, look at the signal-to-noise ratio. A higher ratio means less background noise.
Finally, consider the gain range. Different audio sources need different gain settings. Ensure the line input can provide the necessary gain. This ensures your recordings are clear and distortion-free.
Setting Up And Troubleshooting Line Inputs
Setting up a line input on an audio interface can be easy. But sometimes, things can go wrong. This guide will help you with both setup and troubleshooting. Let’s begin with the basics.
Step-by-step Setup
First, gather your equipment. You will need an audio interface, a computer, and a line-level device. This could be a keyboard or a mixer.
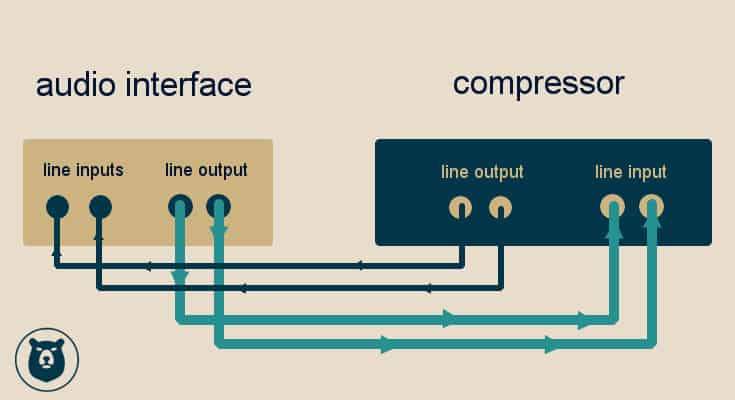
Next, connect your line-level device to the audio interface. Use a 1/4-inch TRS cable for this. Plug one end into the line output of your device. Plug the other end into the line input of the audio interface.
Now, connect the audio interface to your computer. Most interfaces use a USB cable for this. Plug one end into the interface. Plug the other end into your computer’s USB port.
After that, turn on your line-level device and audio interface. Open your audio software on the computer. Check the input settings. Make sure the line input is selected.
Common Issues And Solutions
Sometimes, you might not hear any sound. This could be a simple fix. First, check all your connections. Ensure everything is plugged in correctly.
If the connections are fine, check the volume levels. Make sure your line-level device and audio interface are not muted. Adjust the input gain on your audio interface.
Another issue could be software settings. Open your audio software and check the input settings. Make sure the correct input is selected.
If you still have problems, restart your computer and audio interface. This can often solve unexpected issues. If nothing works, consult your audio interface’s manual or customer support.

Credit: saramonicusa.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Line Input?
A line input on an audio interface allows you to connect external audio sources. These sources can include instruments, mixers, or other audio devices.
How Does Line Input Work?
Line input works by receiving audio signals from connected devices. These signals are then processed and converted to digital format by the audio interface.
Difference Between Line Input And Mic Input?
Line inputs handle higher-level signals, while mic inputs are designed for lower-level microphone signals. This ensures proper signal processing.
Can I Connect A Guitar To A Line Input?
You should avoid connecting a guitar directly to a line input. Use a DI box or instrument input instead.
Conclusion
Understanding the line input on an audio interface is crucial. It connects external devices. This includes instruments and other audio sources. It ensures clean, high-quality sound recordings. Choose the right audio interface for your needs. Consider the number of line inputs required.
This enhances your recording experience. Remember, the right setup impacts your audio quality. So, invest wisely. By knowing your tools, you achieve better results. Happy recording!
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is a line input?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “A line input on an audio interface allows you to connect external audio sources. These sources can include instruments, mixers, or other audio devices.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How does line input work?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Line input works by receiving audio signals from connected devices. These signals are then processed and converted to digital format by the audio interface.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Difference between line input and mic input?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Line inputs handle higher-level signals, while mic inputs are designed for lower-level microphone signals. This ensures proper signal processing.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Can I connect a guitar to a line input?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “You should avoid connecting a guitar directly to a line input. Use a DI box or instrument input instead.” } } ] }As an Amazon Associate, Cleanestor earns from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.

